This article highlights the probable homoeopathic genus epidemicus based on the data collected from the care takers of the affected victims in Calicut, Kerala of South India after detailed study and discussion by RAECH – Rapid Action Epidemic Cell Homoeopathy Govt of Kerala
Compiled by Dr Mansoor Ali
Nipah virus (NiV) was initially isolated and identified in 1999 during an outbreak of encephalitis and respiratory illness among pig farmers and people with close contact with pigs in Malaysia and Singapore. Its name originated from Sungai Nipah, a village in the Malaysian Peninsula where pig farmers became ill with encephalitis. Given the relatedness of NiV to Hendra virus, bat species were quickly singled out for investigation and flying foxes of the genus Pteropus were subsequently identified as the reservoir for NiV
Transmission of Nipah virus to humans may occur after direct contact with infected bats, infected pigs, or from other NiV infected people.
Signs & Symptoms
Infection with Nipah virus is associated with encephalitis (inflammation of the brain). After exposure and an incubation period of 5 to 14 days,illness presents with 3-14 days of fever and headache, followed by drowsiness, disorientation and mental confusion. These signs and symptoms can progress to coma within 24-48 hours. Some patients have a respiratory illness during the early part of their infections, and half of the patients showing severe neurological signs showed also pulmonary signs
Diagnosis
Virus isolation attempts and real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from throat and nasal swabs, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and blood should be performed in the early stages of disease. Antibody detection by ELISA (IgG and IgM) can be used later on. In fatal cases, immunohistochemistry on tissues collected during autopsy may be the only way to confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment in conventional medicine
Treatment is limited to supportive care. Because Nipah virus encephalitis can be transmitted person-to-person, standard infection control practices and proper barrier nursing techniques are important in preventing hospital-acquired infections (nosocomial transmission).
Prevention
Nipah virus infection can be prevented by avoiding exposure to sick individuals,pigs and bats in endemic areas. Avoiding personal contacts is the best option.
Source : https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/nipah/index.html
Lesson from Andhra Pradesh- BCT programme
Between 1993 and 1999 there were 5308 recorded cases of Jpanees encephalitis in the state, of which 1511 resulted in fatalities. The Government of Andhra Pradesh recruited homeopaths to help curb the JE epidemic at a mass scale in 1999.
After the commencement of BCT (Belladona, Calc Carb & Tuberculinum) in 1999 in Andhrpardesh, both mortality and morbidity rates of JE fell significantly. A total of 343 cases were reported in 2000 with 72 deaths, in 2001 only 30 cases with 4 deaths, in 2002 only 18 cases but no deaths, in 2003 and 2004 no cases were recorded. The Government had officially published the statistics and acknowledged the efficacy of homeopathy. This is the first major involvement of homeopathy in the field of prevention of epidemic diseases in our country.
Neighbouring states which have not adopted this method continued to show higher incidence of JE cases. After witnessing the decline in India other nations are showing keen interest in this innovative method.
Currently homoeopathy donot have a specific curative treatment for Nipah virus infection. But we can manage and help the public to a great extened by giving genus epidemicus. Based on the data collected from care takers in Calicut, Kerala – after detailed study and discussion with experts of RAECH, on the principles of homoeopathy GE,we worked out the following symptoms and found the probable Genus Epidemicus as par with BCT programme in Andhra Pradesh.
Verat vird seems to be a remedy that covers major symptoms of Nipah Virus infection
The main symptom found in patients in Calicut Kerala
- Fever with intense heat and chilliness
- Delirium
- Severe Head ache
- Suppression of urine
- Symptoms of encephalitis
- Unconsciousness and coma within hours
- Perspiration in diffrent parts of body
- Rapid pulse in different parts of body
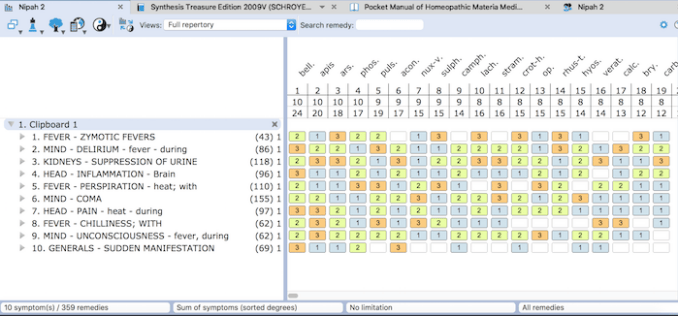
Rubrics Selected ( Synthesis Repertory)
- Fever – Zymotic
- Mind – Delirium Fever during
- Kidney – Suppression Urine
- Head – Inflammation- brain
- Fever – perspiration heat with
- Mind – Coma
- Head – Pain heat during
- Fever – Chilliness with
- Mind- Unconsciousness
- General – Sudden Manifestations
- Perspiration : Single parts
- Pulse Rapid Tachycardia Chill during – Complete repertory
Final marks
Bell : 28/12
Ars : 22/12
Apis : 21/11
Phos : 21/12
Medicine,Dose and Repetition – RAECH Kerala protocol
Belladonna 30 – 4 pills twice daily for 5 days (For children upto 12 years 2 pill twice daily)
On 6th day : Calc Carb 200 2 dose (1 grain)
If epidemic continue can continue Bell 30 every 3rd day after the sixth day (Scarlatina by Hahnemann)
IHMA study report on Nipah epidemic in Kerala
Department of Homoeopathy order on Genus Epidemic distribution
Materia Medica based fever case format
Repertorisation Grid

Sir, Any PREVENTIVE MEDICINE/DRUG IN HOMEO please may be intimated.
Very educative. Thanks