ABSTRACT: Melasma is an acquired pigmentary disorder of skin. Most of the cases are due sunlight exposure and hormones but ignored factors are genetics, cosmetics and phenytoin therapy. Here we discuss into pathology, progress and control of disease process. Role of vitamin c in treatment is main objective, along with homoeopathic drugs. Vitamin C is an antioxidant, blocks reactive oxygen species and thus protect from oxidative stress.
Keywords: Melasma, vitamin c, antioxidant, sunlight, sunscreen, depigmenting agent
Introduction
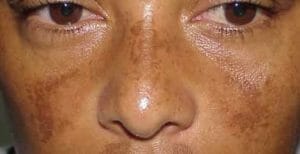
Melasma is an acquired , circumscribed pigmentary disorder characterized by more or less symmetrically distributed, medium to dark brown macules with defined geographical borders; affecting sun exposed areas, particularly to females. Typically affects women of reproductive age due hormonal imbalance. Modern treatment mainly includes hydroquinone, triple combination creams, kojic acid, azelaic acid, arbutin, ascorbic acid, chemical peels and lasers. Some botanical extracts like grape seed extract, green tea extract etc. now in use. Vitamin C is known for its depigmenting property since long time. Vitamin C usually used as home remedies to clear skin. Here in detail we will study various ways to use vitamin c in treatment of melasma.
Epidemiology
It is Common skin condition among darker individual including Indians. 50-70% of melasma occurs during pregnancy. In men though not very common (20.5-25.83%) due to decrease in testosterone levels, use of mustard oil on face and diethylstilboestrol therapy for prostate cancer.
Etiology
- Sunlight: typical affection of sun exposed areas. Long wavelength ultraviolent A and visible light both are able to increase pigmentation especially in individual with dark skin.
- Hormonal: related to oral contraceptives, pregnancy and endocrine disorder. Increase LH and decrease estradiol causes melasma.
- Genetic: occurrence of familial cases.
- Toxic (cosmetics): characteristic affection of face and areas where they are applied.
- Drugs: following phenytoin therapy
Pathogenesis
Due to causative exposure, melanocytes increase in number and activity, with an associated increase in the formation, size and melanization of melanosomes. Prolonged UV (sunlight) exposure-induced dermal inflammation and fibroblast activation leads to increase melanogenesis.
Lipid metabolism got affected in melasma. There is downregulation of lipid metabolism genes like peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR), arachidonate 15- lipoxygenase, PPAR gamma coactivator 1 alpha type B (ALXO 15B), diacylglycerol o-acyltransferase 2-like 3; due to chronic UV rays exposure.
Another change found in melasma on biopsy is thinning of stratum cornuem, along with loss of lipid barrier.
Classification
Melasma is classified as clinical and histopathological. Describing here only about clinical, according to distribution on skin:
- Central fascial pattern 63%: cheeks,forehead,upper lips, nose and chin
- Malar pattern 21%- cheeks and nose
- Mandibular pattern 16%- ramus of mandible
Treatment
General measures
Avoidance of sun exposure, discontinue provocating factors and use of sunscreen.
ROLE OF VITAMIN C
It is a potent antioxidant that can be used topically in dermatology. Naturally found in citrus fruits, strawberries, papaya, broccoli, green leafy vegetables etc. vitamin c is unstable and difficult to deliver to dermis, hence newer products are coming.
— USES OF VITAMIN C
- Vitamin C as antioxidant: when skin is exposed to UV light, ROS such as superoxide ion, peroxide ions are generated. Vitamin c helps by donating electron to neutralize the free radicals.
- C and photo protection: ROS upgrade transcription factor activator protien‑1 (AP‑1) that increases matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) production, leading to collage breakdown. 2] It is important to note that Vit. C is equally effective against both UVB (290-320 nm) and UVA (320-400 nm).it has a UV protective effect by killing free radicals.
- Vitamin C as depigmenting agent: vitamin C interacts with copper ion at the tryosinase active site and inhibits action of enzyme tryosinase, thereby decreasing melanin formation.
- Vitamin C as anti-inflammatory: Vit. C inhibits NFkB, which is responsible for the activation of a number of pro‑inflammatory cytokines such as TNF‑alfa, IL1, and IL6 etc.
- Vitamin C in collagen synthesis: it act as a cofactor and stimulate collagen gene formation, thus it increases collagen production in both young and old skin.
FORMULATION OF VITAMIN C
- Vitamin C serum
- Vitamin C creams
- Sunscreen with vitamin C
- Vitamin C +E creams
HOME REMEDY
- Lemon mix with glycerin and rose water. Concentration of lemon juice should be ¼ of all as it can cause irritation
- Orange juice mixed with glycerin.
- Honey and lemon juice .

Be the first to comment